

Options for retirement accounts offer incredible flexibility in investing and can be a powerful addition for investors interested in more advanced trading and investing strategies.
Options provide an ability to potentially increase income, hedge risk, and leverage up existing positions.
However, when used in a retirement account, they come with unique risks, rules, and regulations.
This article will explore the basics of options, their benefits and risks in an IRA account, and some potential strategies to use in a retirement account.
Contents
The Basics Of Options
First, let’s do a quick recap of the basics of options.
Options are derivative contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined “strike” price on or before a given date.
Call options give the right to buy, and put options give the right to sell.
Common strategies include using calls and puts for directional trades and hedges, credit spreads, and covered calls/cash-secured puts for income generation.
Properly used, options offer the investor abilities and flexibility that can not be dreamed of with just equities and bonds alone.
Still, they come with unique complexities and risks, so being well-educated is crucial for long-term success.
Options In An IRA.
While permitted, trading options within IRAs involves adhering to specific rules and regulations of governing bodies and your retirement plans administrator.
Most brokerages require investors to apply for approval before options can be traded in an IRA.
These approvals often have steps or levels to them. Level 0 or 1, depending on your broker, is usually covered calls, protective puts, collars, and cash-secured puts.
These are all fairly “safe” strategies, requiring either stock or cash for collateral for the trade.
They also share that they are the simplest to learn relative to the amount of risk you take.
The odds of your trade going to zero on a covered call are significantly less than if you just bought naked calls.
The next level up will usually be purchasing naked puts and calls and straddles and strangles (variations on owning both a put and call).
These carry substantially more risk of a position going to zero.
Finally, there is the top level, which is often various types of spreads such as verticals (credit spreads), butterflies, and condors.
These spreads require some advanced knowledge to open and manage, so this level of trading often requires an additional application process through your IRA or Broker.
Retirement accounts prohibit any unlimited risk trade, such as selling a naked call.
All cash or securities to cover options obligations must be held within the IRA account.
Also, any profits derived from options trades inside a retirement account receive the same tax-deferred benefits as any other trade behind the tax threshold.
Popular Strategies For IRA Accounts
Now that we have gone over the basics let’s jump into some of the more popular strategies used in Retirement accounts.
Covered Calls
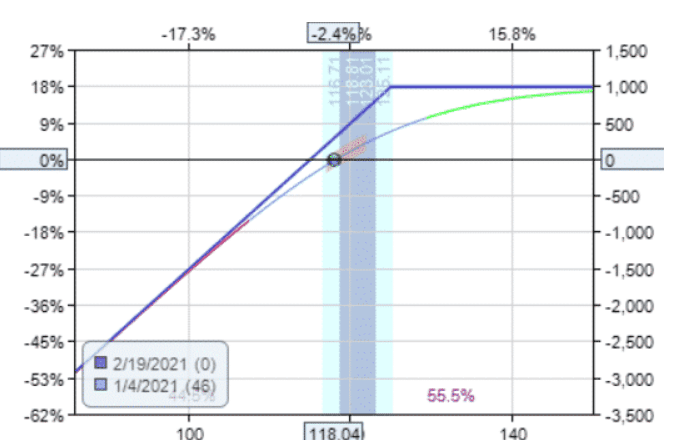
Covered calls are probably the most utilized option strategy.
It involves selling call options against shares already owned in the retirement account to collect the premium as income.
This strategy allows the investor to increase the yield on dividend stocks and create yield on non-dividend paying stocks.
The tradeoff is that the sold call caps any potential price appreciation.
These often work well on stable blue-chip stocks that don’t have violent price fluctuations.
Cash Secured Puts
Cash-secured puts are another income-producing strategy, but they have a bonus.
They allow investors to get paid to potentially buy a stock at a lower price.
These would work the same as in a regular brokerage account; you want to purchase stock ABC at $65/share, but it’s currently trading at $75.
You Sell a $65 put for a month out and collect the premium on the option.
In return, the cash required to purchase the shares at $65 is held as collateral.
In the worst case, you purchase a stock you wanted at a discount; in the best-case scenario, you continue to earn a yield on idle capital.
Verticals
Verticals are a fixed-risk/fixed-reward directional trade that involves buying and selling a put or call.
These can be either a credit or debit spread but are most commonly used to collect premiums while directionally trading a stock.
The benefit of a vertical is that you are solely basing your trade on direction.
You keep the premium as long as the price closes above or below the outside strike.
It can be a fantastic income generator for active investors with idle capital.
Protective Put
A protective put is probably the purest use for an option contract in a retirement account.
The protective put does just what the name suggests: it protects your equity position.
This is placed by purchasing and out of the money (strike is lower than the current price) put for every 100 shares of stock you own.
This caps your potential loss if the market or stock declines but keeps your upside potential uncapped. Your maximum risk is just the premium paid for the put.
It’s like an inexpensive insurance policy for your shares.
Benefits of Using Options in Retirement Accounts
In the right circumstances, options offer some significant advantages in a retirement account:
- Income generation – Premium earned from credit spreads, cash-secured puts, and covered calls help to create income and return on idle assets.
- Risk management – Strategies like collars, protective puts, and debit spreads cap maximum losses on individual trades and on equity positions.
- Leverage – Options can offer outsized returns on capital due to leverage, but this leverage is a double-edged sword.
- Tax benefits – Additional profits receive the same tax treatment as the rest of the account.
Risks of Using Options in Retirement Accounts
While they can be hugely beneficial to your account, some unique risks come with using options in a Retirement account:
- Tax implications – Wash sales or capital losses lose the beneficial tax treatment on those trades and possibly incur penalties.
- Restrictions – While governmental guidelines exist on what is allowed in a retirement account, individual brokers may further restrict your abilities depending on your skill level and account.
- Speculation – Over-leveraging and excessive speculation can lead to significant losses in your account.
With the proper education and management, options can be an incredibly effective addition to your retirement account.
Focus on defined risk, protection, and income strategies over speculation to use them to their complete potential.
One thing to be aware of is the potential tax implication of wash sales and capital losses.
But used correctly, options provide a means to diversify and potentially enhance retirement savings.
We hope you enjoyed this article on using options for retirement.
If you have any questions, please send an email or leave a comment below.
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.










