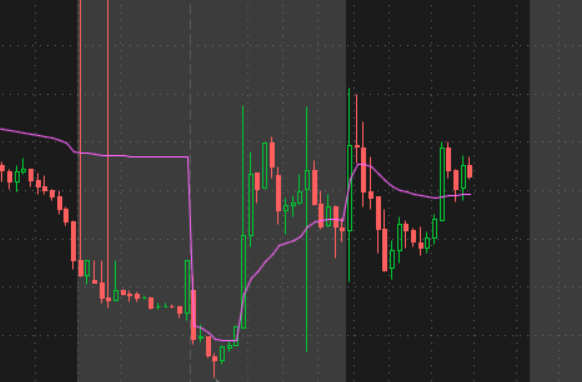
Today we’re looking at a VWAP Trading Strategy.
VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price and is a popular trading strategy both new and expert traders use.
It works by taking the daily volume of a stock and dividing it by the total amount traded to calculate the security’s average price.
Contents
- Introduction
- Basics of VWAP
- The Importance of Volume
- Identifying Potential Entry and Exit Points
- VWAP For Rangebound Trading
- Tips For Implementing VWAP Trading Strategies
- Conclusion
Introduction
The VWAP trading strategy allows traders to identify potential entry and exit points and also helps to identify potential breakouts and reversals.
This guide will take a closer look at VWAP trading strategies and provide an in-depth understanding of how to use the VWAP indicator to your advantage.
We’ll look at the basics, the importance of volume, and the different VWAP trading strategies.
Basics of VWAP
VWAP is a basic indicator that’s easy to understand.
Traders use it to identify potential entry and exit points as well as identify potential breakouts and reversals.
Traders will calculate the volume of the security and then divide it by the total amount traded to get the average price.
The average price is typically calculated from a 24-hour period but can also be calculated from a weekly or monthly period.
It can also be used on smaller timeframes, but it becomes less meaningful the lower the timeframe is. It’s also important to note that VWAP isn’t strictly for active traders.
Passive investors can also use larger timeframes to look for where a lot of trading is being done.
Any VWAP trading strategy will work best when combined with other indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and/or the Moving Average Convergence-Divergence (MACD).
The Importance of Volume
Volume is the central driver for VWAP, so the more volume you have, the more accurate the indicator will be.
Volume is important because it indicates how actively a stock is traded and your VWAP will be more accurate.
For example, if you’re using a VWAP strategy on a stock that has very low volume, it is possible that the stock will spike or drop on lower volume making your VWAP calculations inaccurate at best.
If you are using it for trading actively, this can be a problem as it will not identify entries and exists correctly.
It is a good practice to make sure your trading instruments always have good volume, though low floats can be dangerous.
Identifying Potential Entry and Exit Points
When using the VWAP, one of the best ways to identify potential entry and exit points is to look for price action near the line.
This can help identify potential breakouts and potential reversals.
For example, if you’re looking to buy a security, you can wait for the price to break above the VWAP line, then look for confirmation on a secondary indicator that fits your trading plan.
Similarly, if you’re looking to sell a security, you can wait for the price to break below the VWAP line and look for a similar confirmation.
As with all trading strategies, it is important to remember nothing is 100%, so make sure your risk management works for you.
It’s best used as a way to confirm your existing trading strategy rather than as a standalone trading strategy.
The closer you get to the VWAP line, the riskier your trade becomes because it could signal you are on the wrong side if it breaks through.
VWAP For Rangebound Trading
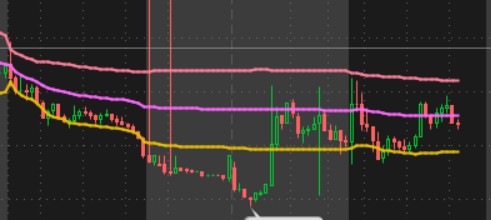
Another fairly common way to use VWAP is using the bands that often accompany it.
These bands are usually x amount of standard deviations away from VWAP, which makes them also most like Bollinger bands.
This is important because often times the further price gets away from the average, the better the odds it rejects back to it.
Obviously, this is not always the case.
There are plenty of times that price trends in one direction and does not care at all about volume, averages, or anything.
But on the days that this isn’t the case, the VWAP Bands can provide some excellent short-term signals.
This strategy also works on larger timeframes but would require different risk management on each time frame.
See the picture below for an example of VWAP Bands.
Tips For Implementing VWAP Trading Strategies
– Always remember that no one-size-fits-all strategy works well with all types of markets. It’s important to have multiple strategies for multiple market types. Using VWAP is no different.
– Timeframes matter with VWAP. The higher the time frame, the more reliable the indicator is.
– VWAP is best used as a support indicator. While it has a lot of potential, it’s best used in conjunction with another indicator or as part of a general strategy as opposed to a standalone system.
– Volume is important. You need to ensure the instrument you trade has consistent volume throughout the session; otherwise, VWAP will display false signals and be unreliable at best.
Conclusion
As you can see, VWAP trading is a very popular strategy that both novice and expert traders can use.
The indicator has a wide range of uses and strategies and can work well in many different types of markets.
We also learned that volume is an important factor in VWAP calculations and that it works best in addition to a trading strategy.
It becomes less reliable as a standalone indicator in most cases.
However, if you trade VWAP, it’s important to make sure that your risk management is sound, as there is no miracle indicator.
We hope your enjoyed this article on the vwap trading strategy. If you have any questions, please send an email or leave a comment below.
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.