

Contents
Welcome to the world of hedging with options!
If you’re in the investments, you’ve probably heard these terms used often, especially going into a news release.
But what exactly are options, and why are they important?
Simply put, options are contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a specified date.
Next up is hedging and why it is important.
Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves taking an offsetting position to reduce a main position’s potential losses or drawdowns.
In other words, it helps investors protect their investments from market volatility.
Now that you know what hedging is, let’s look at how options can help.
Options can offer flexibility and limited risk, often requiring less capital than traditional hedging methods.
Plus, they can be used in a variety of trading strategies.
With these key points in mind, let’s dive into the basics of options and popular hedging strategies using options.
Basic Concepts of Options
If you’re new to options trading or need a quick refresher, it’s essential to understand the basic concepts going into the hedging conversation.
Calls and puts are the two types of options contracts available.
Buying a call option gives investors the right to buy an underlying asset at a fixed price within a given time frame.
On the flip side, a put option gives the holder the right to sell the asset at a predetermined price within the same period.
Then there are intrinsic and extrinsic values and how they affect the option price. In-the-money options have intrinsic value.
This is basically just that the stock price is above the option’s strike price.
Extrinsic value, also known as time value, is the additional premium an option holder pays above the intrinsic value.
It’s possible to have no intrinsic value and only extrinsic value if the option is out of the money and has some time left.
Options expiration is the point where an option contract is no longer valid.
The holder loses the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
Employing standardized contracts ensures all traders adopt a common language in buying or selling options, especially regarding hedging.
Popular Hedging Strategies with Options
Now that we’ve gone over some of the basics of options again, let’s dig into some ways to use them in hedging.
There are many ways to hedge a position; the limit is almost how creative you can actually get.
That being said, here are some of the more popular hedging strategies around.
Long Put
First up is the Long Put strategy.
This is where an investor buys a put option to offset any potential loss in a stock purchase.
If the stock price falls below a certain level, the put option will be exercised, and the investor will sell the underlying asset at the put’s strike price, limiting their losses.
This is one of the most basic and straightforward hedging strategies but extremely effective.
This works especially well once you profit from the equity position.
Below is an example of the risk profile, both without a hedge (left) and with a hedge (right).
As you can see, the risk flattens off, and the bottom of the right picture is where the strike of the option is.
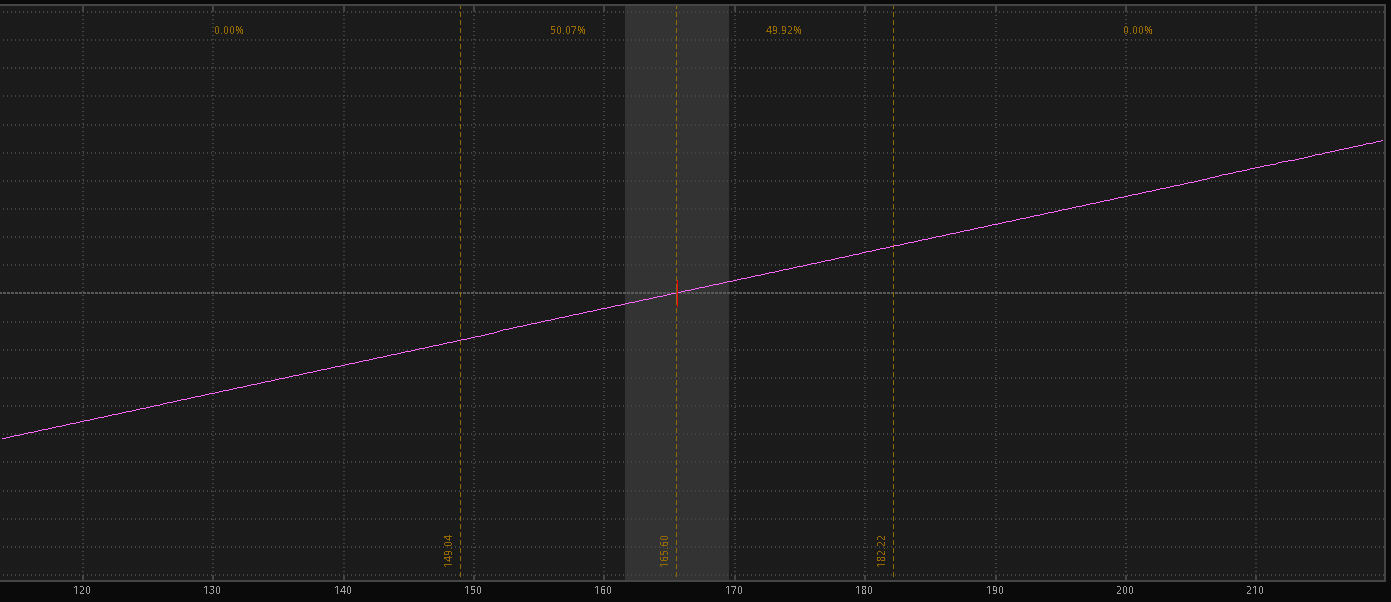
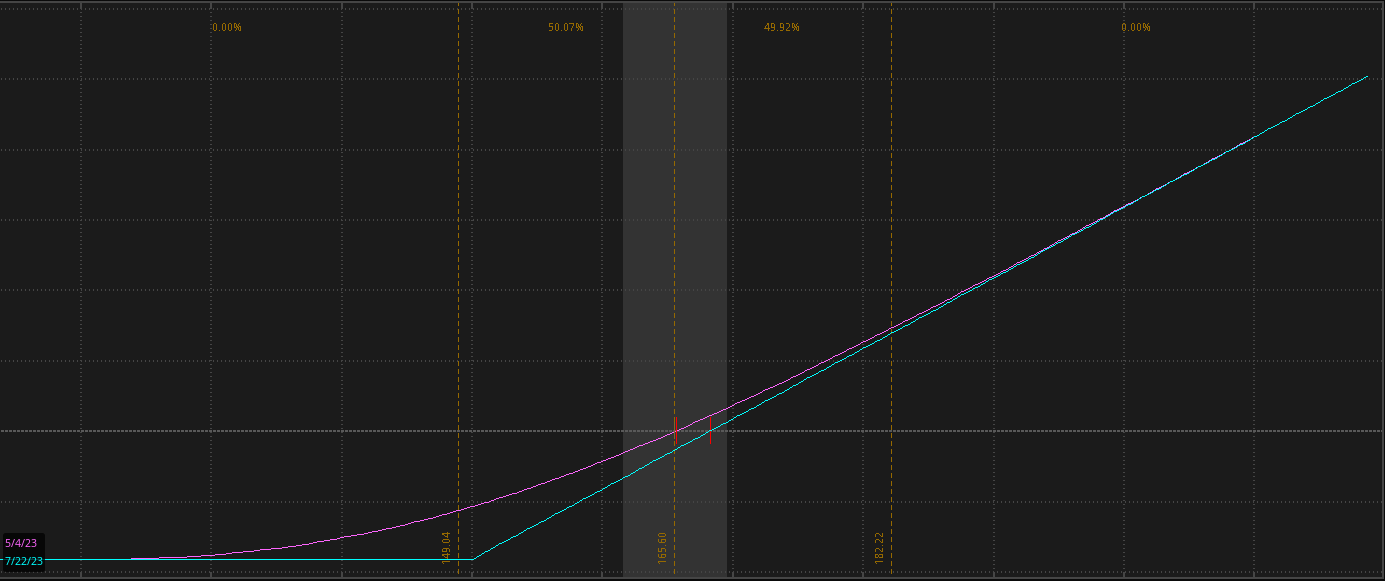
Protective Put
Next up, we have the Protective Put.
This is more or less the same as the Long Put strategy, with the largest difference being the timing.
A protective put is purchased simultaneously with the equity, so it’s similar to a built-in stop loss with a time component.
If the stock price falls below the strike price, the investor can exercise the put, selling the stock at a fixed loss.
Long Call
To Hedge an open short position, we have the Long Call.
This approach requires an investor to buy a call option as a way to offset any potential losses in a short-stock position.
If the stock price rises above the call option’s strike price, investors can exercise the option and buy the underlying asset, limiting their losses.
This works the exact same way a long/protective put works, just in the opposite direction.
The Collar
The final stock protection hedge we have is the Collar.
This involves buying a put option to offset potential losses on an underlying while selling a call option to finance the put purchase.
This strategy is particularly useful when an investor wants to limit their potential losses without giving up all their potential gains.
This is a more advanced hedging strategy as it requires a full option spread in addition to the stock position.
Straddle/Strangle
Finally, we have the Straddle and Strangle strategies.
These approaches involve buying both calls and put options simultaneously at the same strike price (straddle) or different strike prices (strangle), betting on the underlying asset’s volatility.
This is often used as a stand-alone position as it is, in effect, a hedge on each option.
You are protected from a directional move either way.
You can also use this on an equity hedge, but it really only protects against volatility and not a directional move against an underlying position.
Below is an example of a straddle: the call and put share a strike, creating an almost perfect “V” profile.
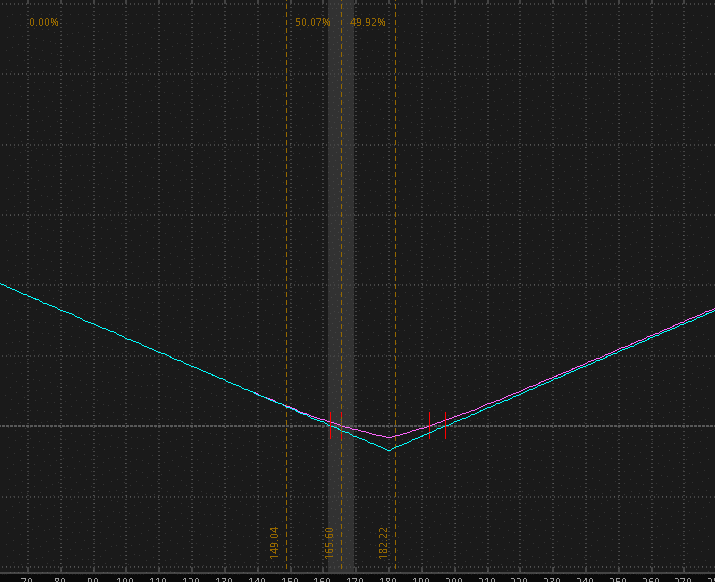
Factors to Consider While Hedging with Options
Hedging with options can be as simple or complex as you would like to make it.
A few factors to consider will help determine the best hedging strategy for you.
Market conditions play a crucial role in deciding the right course of action, as the price movements of different assets can impact each other.
Looking at ranges is a great way to know which kind of hedge to use.
Volatility also plays a significant role in determining the right options to choose, as it is a factor in the amount of premium paid for a contract.
It will also help to determine how far out-of-the-money is and which type of hedge to use.
The more volatile, the more one may want to aim for something like a straddle
The cost of options contracts plays another critical role while hedging with options.
The cost of the hedge needs to be factored into your profit and loss calculation as its more than likely to expire worthless.
Risk tolerance is another factor that must be considered, as greater risk tolerance allows for more aggressive(think out of the money) hedging strategies.
This drives down immediate costs but creates a larger potential loss on an underlying position.
Finally, tax implications can play a role in determining the strategy’s effectiveness, as options trading is taxed differently from other types of investments, so holding duration is a factor.
As with all trading, there is no one-size-fits-all; personal tolerance, holding time, and personal preference will play a large part in your hedging strategy selection.
Expertise with options will also play another.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Options for Hedging
Options trading can be a great way to hedge your positions, but it has drawbacks.
Let’s examine some of the pros and cons of this type of hedging.
Leverage can be both a drawback and a benefit.
While it allows investors to control a large amount of an asset with fewer upfront costs, it can also magnify losses.
This is particularly important to note with a straddle and strangle type position hedge.
Flexibility is a distinct advantage of options trading.
Investors can alter their strategy to meet the amount of risk they are comfortable with.
They can also be used to adjust on the fly as a position moves into or out of profit.
One final potential drawback is the cost.
While the cost is low upfront, most options expire worthless, which means you may need to continually buy protection for your position as one set expires.
Depending on your use case, this may not be a large issue, for instance, if you only want to be hedged into a news event like earnings.
Overall, hedging with options can be a powerful tool, but it’s not perfect.
Investors need to weigh the pros and cons carefully when considering whether to use options as a hedging strategy.
Conclusion
Remember that options are just one tool in your toolbox when it comes to hedging your positions in the market.
Whether you use them or not depends on your risk tolerance, market conditions, proficiency, and personal preferences.
While options can be a powerful tool for protecting your portfolio is important to know what your personal needs are before you enter a hedge.
Individual circumstances will always change, but that is one of the great things about options as a hedge.
There will more than likely be a strategy for you here.
We hope you enjoyed this article about hedging with options.
If you have any questions, please send an email or leave a comment below.
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.










